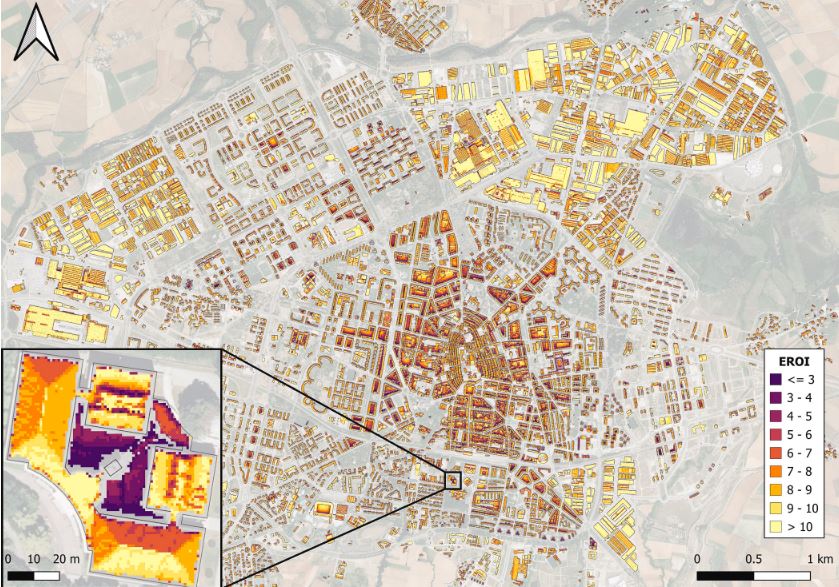
Energy consumption and carbon emissions are concentrated in cities, where 70 % of the global population is projected to live by 2050. Urban environments must therefore be at the heart of any global energy transition. Furthermore, land availability is a limiting factor for renewable deployment and rooftop PV thus offers a clear advantage. This research is based on the rooftop photovoltaic potential (RPVP) of the city of Vitoria-Gasteiz; its ultimate goal is to provide stakeholders with a useful and free tool to calculate a highly accurate RPVP (including different tilt and orientation angles, shadowing, temperature effect, energy return on energy investment (EROI) constraint and available surface area) and based exclusively on free-to-use and open-source software. The EROI constraint is a fundamental step towards the net energy analysis being integrated in the RPVP assessment. This paper is a contribution not only to the application of the EROI constraint, but also to the calculation of this indicator. Results improve on estimates commonly found in the literature. With an EROI > 5 (8.83 on average), Vitoria-Gasteiz has a RPVP of 473 GWh/year, able to supply 38 % of the total electricity consumption of the city and where 50 % of total rooftop area is suitable for PV. Therefore, the rooftop PV performance in Vitoria-Gasteiz is sufficiently good to provide the net energy required to sustain today’s industrial societies. Additionally, this article provides valuable information, such as rooftop usability factors, and an overall reduction factor (CT), useful to extend RPVP assessment to larger areas using constant value methods.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2025.115401